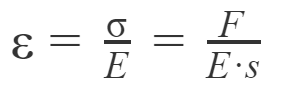What is Young’s modulus?
Young’s modulus, also known as the tensile modulus, elastic modulus or traction modulus (measured in Pa, which is a pressure unit(N.m^-2; 10MPa is equivalent to 1Kg force per square millimeter) is a mechanical property of linear elastic materials. It, evaluates the elasticity of rigid or solid materials, which is the relation between the deformation of a material and the power needed to deform it. For example, a stiff material needs more force to deform compared to a soft material. Rubber has a 1MPa modulus, and iron has a 200GPa modulus (200.000 times more). For the same force applied to a sample with the same thickness, the rubber samples will extend 200.000 times more.
The deformation of a physical object depends first of all on the design geometry. Indeed, it’s easy to understand that a thick piece is harder to deform than a thin one.
The relation between force and deformation is the following :
Where:
-Epsilon is the elongation (Length / original Length) no unit
–Sigma is the stress in PA or PSI
– F is the force in N or lbf
– s is the transverse section in m² or in²
Applying a 400Kilo-force (4000N) to a 2cm radius (0.00126 section) 2 meter long steel rod with a Young’s modulus of 200 GPa, the rod will deform off 4000/(0.00126* 200.000.000)=0.016 and the rod will now measure 2.032m
What is tensile strength?
Tensile strength is the value of the maximum stress that a material can handle. This is the limit between plasticity zone and rupture zone.
It’s important to notice the difference between resistance and elasticity.
A rubber band is easier to deform that a spaghetti but it’s harder to break.
What is elongation at break ?
Elongation at break is the elongation that a material can withstand before breaking.It has no unit.
A rod of 10 cm at rest that is 15 before at break has an elongation at break of 0.5 sometimes written 50%.
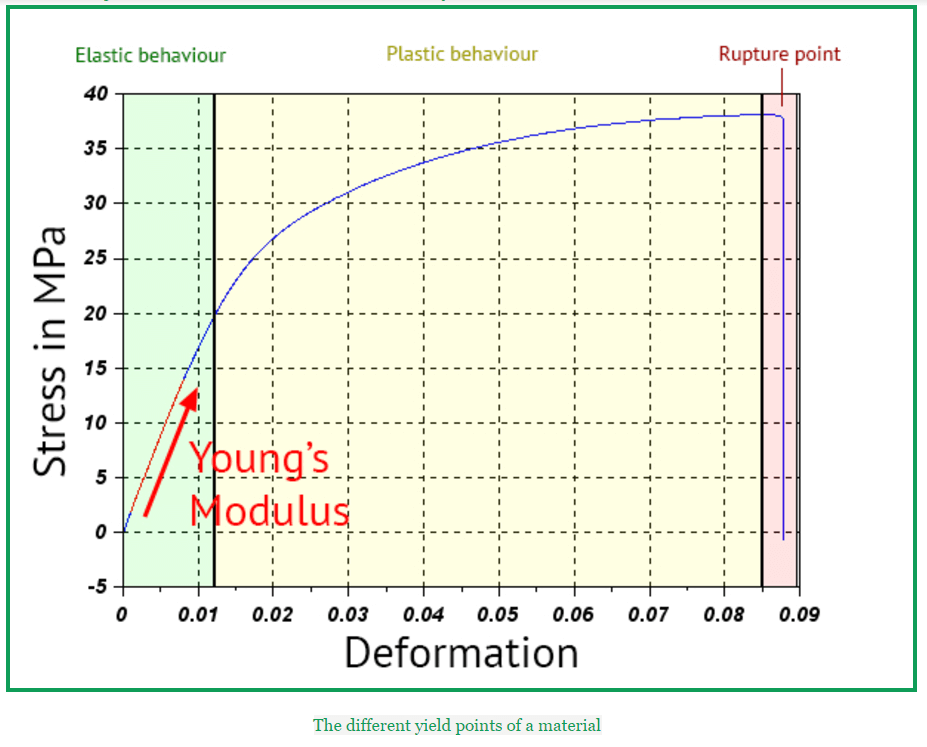
Stress-strain curve
There are mainly 3 types of behavior for a material, depending (among other variables) on the strength you use to deform it. Each of these behaviors are separated by yield points on the engineering stress-strain curve:
- Before the first yield point, the material will have an elastic behavior, which means that it will go back to its initial state if we release the applied strength.
- Beyond the elastic limit, the material will have a plastic behavior, and permanent deformation will occur. For example, modeling clay always has a plastic behavior.
- Finally, if the strength applied is too big, then the material will reach the ultimate strength point rupture point. After this,the This is where it will break, but as it is linked to a lot of variables, such as the geometry of the object, it is difficult to know exactly when it will occur.


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook